The Union Cabinet has approved several significant infrastructure projects and agricultural support measures in its recent meeting, demonstrating the government’s commitment to balanced regional development and economic growth across various sectors.
Shillong-Silchar Highway Corridor: Transforming Northeast Connectivity
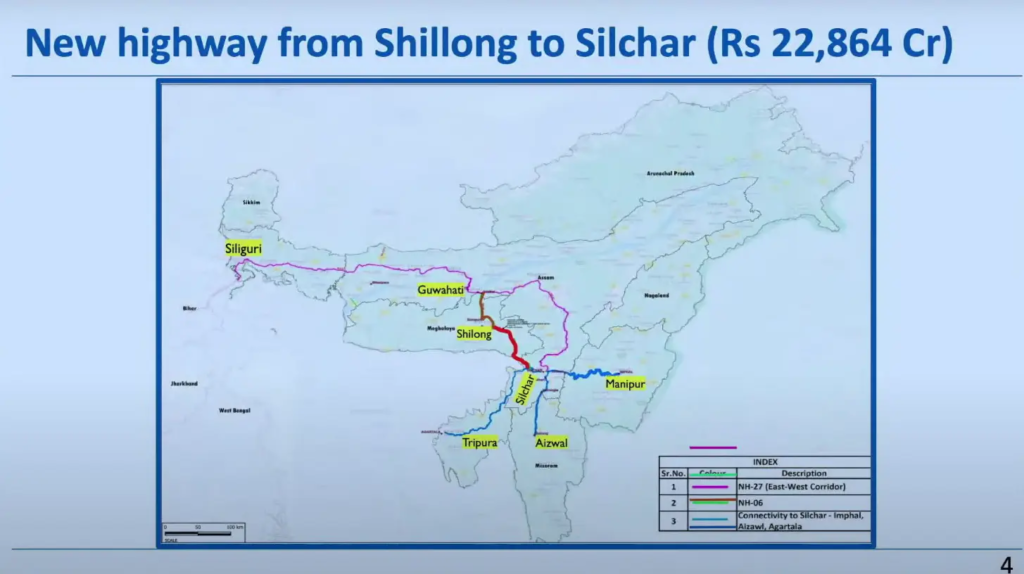
Image Source: Ministry of Information and Broadcasting Official Website
A landmark 4-lane high-speed corridor connecting Shillong (Meghalaya) to Silchar (Assam) has been approved at a cost of Rs 22,864 crore. This 166.8 km strategic highway will be developed under the Hybrid Annuity Mode with a 3-year construction period followed by a 15-year operation period.
The corridor includes impressive infrastructure components:
- 19 major bridges
- 153 minor bridges
- 326 culverts
- 22 underpasses
- 26 overpasses
- 34 viaducts spanning 9 km
This project holds immense strategic importance as Silchar serves as a crucial entry point connecting Mizoram, Tripura, and Manipur, as well as the Barak Valley region of Assam. The Guwahati-Shillong-Silchar route is preferred by traffic as the shortest connection, and NH-6 will become the major connectivity project for the entire Northeast region.
Comprehensive Infrastructure Development Plan
The Cabinet has approved a massive infrastructure development plan worth Rs 10,18,778 crore across multiple sectors:
Airport Development (Rs 5,832 Cr)
- Bagdogra, Bihta, and Varanasi airports
Port Development (Rs 76,220 Cr)
- Major port at Vadhavan near Dahanu in Maharashtra
Highway Projects (Rs 1,58,141 Cr)
- 8 National High-Speed Road projects spanning 936 km
- PM Gram Sadak Yojana
- Border area roads in Punjab and Rajasthan
- Six-lane highway connecting JNPT
- Four-lane Patna-Arrah-Sasaram Corridor
- Six-lane Zirakpur bypass
- Four-lane Shillong-Silchar corridor
Railway Development (Rs 86,507 Cr)
- 22 Railway projects including 1,333 km new lines and 1,536 km multi-tracking
- New bridge in Varanasi
Metro Rail Projects (Rs 1,00,242 Cr)
- 2 corridors of Bangalore Metro (44.65 km)
- Thane Ring Metro (29 km)
- Pune Metro Phase-I (5.46 km)
- Chennai Metro Phase 2
- Delhi Metro Phase 4
Industrial Development (Rs 28,602 Cr)
- 12 industrial smart cities
Housing (Rs 5,36,137 Cr)
- PM Awaas Yojana (1 crore urban houses and 2 crore rural houses)
Hydroelectric Projects (Rs 20,286 Cr)
- Enabling infrastructure for hydroelectric projects
- Financial assistance for equity participation by Northeastern state governments
- 2 projects on Yarjep river
Ropeways (Rs 6,811 Cr)
- Kedarnath and Hemkund Sahib ropeways in Uttarakhand
Fair and Remunerative Price for Sugarcane 2025
The Cabinet has approved the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) for sugarcane at Rs 355 per quintal for the 2025 sugar season, based on recommendations from the Commission for Agricultural Costs & Prices (CACP). This price is set for a basic recovery level of 10.25%.
The FRP mechanism includes:
- For every 0.1% increase in recovery above 10.25%, FRP increases by Rs 3.46 per quintal
- For every 0.1% decline in recovery below 10.25%, FRP reduces by Rs 3.46 per quintal, but only up to 9.5%
- At recovery level 9.5% and below, FRP will be Rs 329.05 per quintal
The approved FRP represents 105.2% over the all-India weighted average cost of production (Rs 173 per quintal), ensuring farmers receive fair compensation for their produce.
For context, in 2023-24, Rs 1,11,701 crore was paid to farmers, with 3,190 lakh metric tonnes of sugarcane crushed, resulting in 320 lakh metric tonnes of sugar production.
The FRP is a benchmark price below which no sugar factory can purchase sugarcane from farmers. It is fixed under the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966, considering factors such as production costs, reasonable margins for growers, recovery rates, consumer sugar prices, market prices by producers, and revenue from by-products like molasses, bagasse, and press mud.
Series of Decisions for Farmers’ Welfare: A Major Push for Indian Agriculture (2024-25)
The Government of India has recently announced a comprehensive series of cabinet decisions aimed at transforming the agricultural landscape and improving the welfare of farmers across the country. With a combined investment of over ₹2.3 lakh crore, these initiatives focus on enhancing productivity, sustainability, and income security for millions of Indian farmers. Here’s a detailed look at the key decisions and their expected impact.
1. MSP for Kharif Crops for Marketing Season 2024-25
Allocation: ₹2,00,799 crore
The government’s commitment to Minimum Support Price (MSP) ensures that farmers receive fair and remunerative prices for their produce. This massive allocation for Kharif crops will provide direct financial security and stability to farmers, encouraging them to invest in better inputs and technology.
2. Clean Plant Programme (CPP) for Development of Horticulture
Allocation: ₹1,766 crore
The CPP focuses on supplying disease-free, high-quality planting material to horticulture farmers. This will boost productivity, improve crop quality, and open up new export opportunities for Indian fruits and vegetables.
3. Expansion of Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
Allocation: ₹10,736 crore
This fund supports the creation of modern infrastructure such as warehouses, cold storage, and processing units. Improved infrastructure will reduce post-harvest losses and enhance farmers’ access to markets.
4. PM JI-VAN Yojana – Financial Support for Advanced Biofuel Projects
Allocation: ₹1,969 crore
By promoting advanced biofuel projects, this scheme aims to provide alternative income sources for farmers through the supply of agricultural residues and waste for biofuel production.
5. BioE3 (Biotech for Economy, Environment, and Employment) for Biomanufacturing
Allocation: ₹1,500 crore
BioE3 will foster innovation in biomanufacturing, creating new employment opportunities and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
6. Digital Agricultural Mission
Allocation: ₹2,817 crore
This mission will harness digital technologies-such as AI, IoT, and data analytics-to modernize farming practices, improve efficiency, and provide real-time advisory services to farmers.
7. Crop Science for Food and Nutritional Security
Allocation: ₹3,979 crore
Investments in crop science will drive research and development of high-yielding, climate-resilient, and nutritionally rich crop varieties, ensuring food security for the nation.
8. Strengthening Agriculture Education & Management
Allocation: ₹2,291 crore
This initiative aims to upgrade agricultural universities and institutions, enhancing the quality of education and research in the sector.
9. Sustainable Livestock Health and Production
Allocation: ₹1,702 crore
Focused on improving animal health and productivity, this scheme will help increase farmers’ income from livestock and ensure the supply of quality animal products.
10. Sustainable Development of Horticulture
Allocation: ₹1,125 crore
This program will promote eco-friendly horticultural practices, water conservation, and the adoption of new technologies for higher yields.
11. Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK)
Allocation: ₹1,202 crore
KVKs are crucial for transferring new technologies and best practices to farmers at the grassroots level. This funding will enhance their outreach and effectiveness.
12. Natural Resource Management
Allocation: ₹1,115 crore
Sustainable management of soil, water, and other natural resources is essential for long-term agricultural growth. This initiative will support conservation and efficient utilization of resources.
Summary Table
| Decision | Details |
|---|---|
| Shillong–Silchar Corridor | 166.8 km, ₹22,864 crore, NH-06, Hybrid Annuity Mode, boosts NE connectivity and logistics |
| Sugarcane FRP for 2025–26 | ₹355/quintal (10.25% recovery), 4.41% hike, applies from Oct 2025, protects farmer interests |
| Other Infra Projects (April 2025) | Tirupati–Katpadi railway doubling, Zirakpur bypass, irrigation modernization (total ₹4,800+ cr) |















