Kerala is grappling with an unprecedented drug crisis, with 27,701 NDPS Act cases in 2024 – three times higher than Punjab’s 9,025 cases. The state government has launched aggressive enforcement measures, but synthetic drugs, organized networks, and rising youth addiction pose major challenges.
Contents
Summary of Kerala’s Drug Crisis and Responses
- Scale: 78 drug cases per lakh population in Kerala vs. 30 in Punjab.
- Enforcement: Over 27,000 arrests in 2024, with a 98.9% conviction rate.
- Key Threats: MDMA, methamphetamine, and LSD dominate the market, with hyperlocal trafficking networks.
- Public Anger: Vigilante committees and panchayats offering rewards for reporting peddlers.

Measures Taken by the Kerala Government
- Operation D-Hunt
- Joint police-excise task force arresting 2,854 suspects and seizing 14+ kg of MDMA (2022–2024).
- Vimukthi Mission: Statewide anti-drug awareness campaigns in schools/colleges.
- Inter-State Collaboration
- Partnership with 5 states and 2 UTs to dismantle supply chains, leading to:
- 128 kg cannabis seized in Tamil Nadu.
- MDMA supplier busts in Andhra Pradesh.
- Partnership with 5 states and 2 UTs to dismantle supply chains, leading to:
- Legal Strictness
- 98.34% conviction rate in 2023 for NDPS cases, far above India’s 75% average.
- Repeat offenders face preventive detention under the NDPS Act.
- Technology and Surveillance
- Cyber-police monitoring dark web transactions.
- WhatsApp groups for real-time coordination between state agencies .

Role of Vigilante Committees
- Street Justice: Groups in Malappuram and elsewhere physically target suspected peddlers.
- Whistleblower Rewards: ₹10,000 cash incentives for reporting drug activity.
- Criticism: Focus on low-level users instead of cartels, potentially aiding syndicates.
Effectiveness of De-Addiction Centers
- Sober Villa Model: Holistic rehab programs report success, but statewide infrastructure remains inadequate.
- Government Initiatives: Telemedicine and vocational training introduced, yet relapse rates stay high.
- 2024 Stats: 588 children sought rehab in 2 months, prompting a new “Kerala Model” anti-drug campaign.
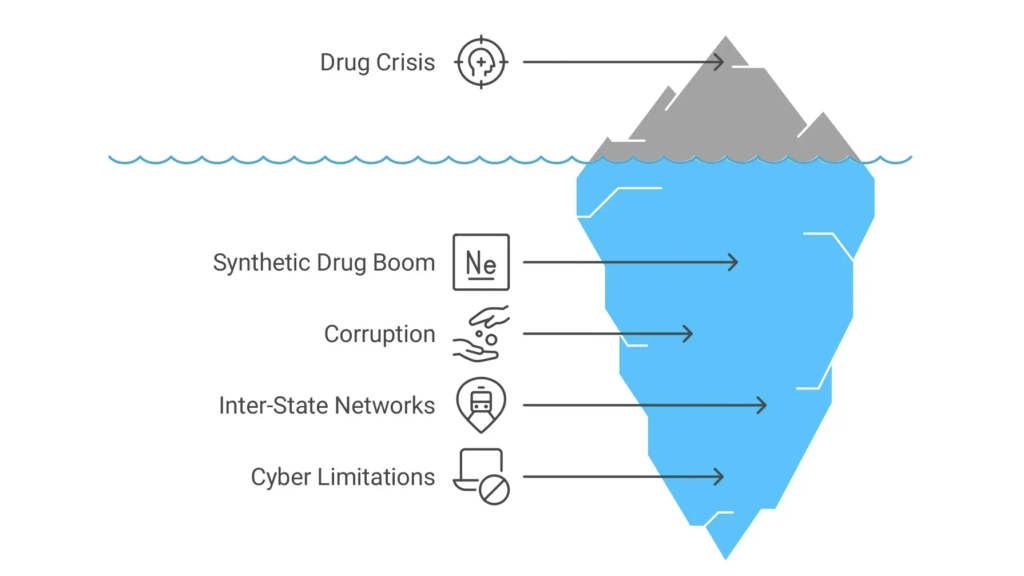
Law Enforcement Challenges
- Synthetic Drug Boom: MDMA/LSD labs are harder to trace than traditional cannabis.
- Corruption: Low-ranking officials allegedly leak raid plans to trafficker .
- Inter-State Networks: Drugs enter via land (Karnataka/Tamil Nadu) and sea (Lakshadweep).
- Cyber Limitations: Poor coordination between excise and police cyber wings delays investigations.
Conclusion
Kerala’s drug crisis outpaces Punjab’s in scale, driven by synthetic substances and urban-rural spread. While enforcement wins praise for high conviction rates, vigilantism and rehab gaps underscore the need for systemic reforms. The state’s fight now hinges on disrupting supply chains beyond its borders and addressing socio-economic triggers of addiction.















